Biomedical AI Projects
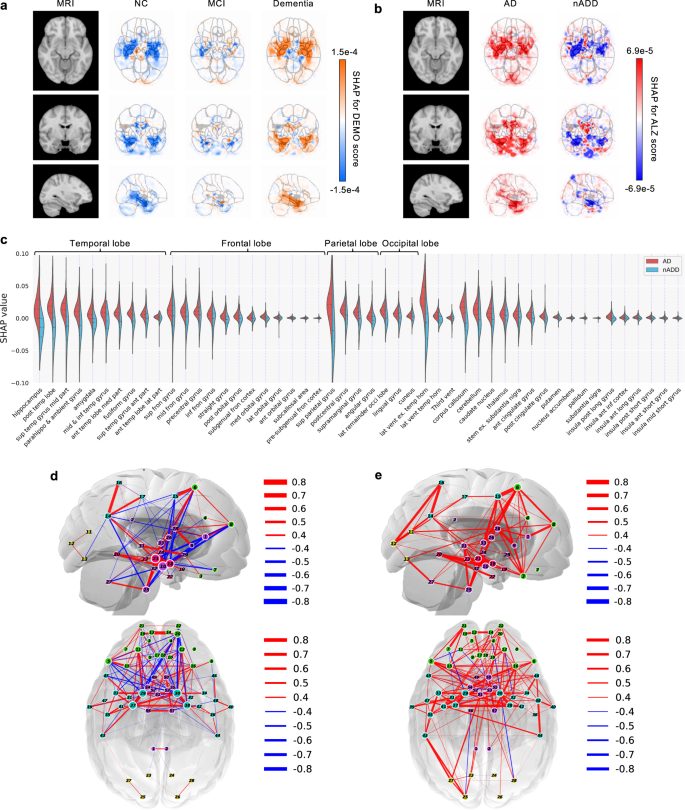
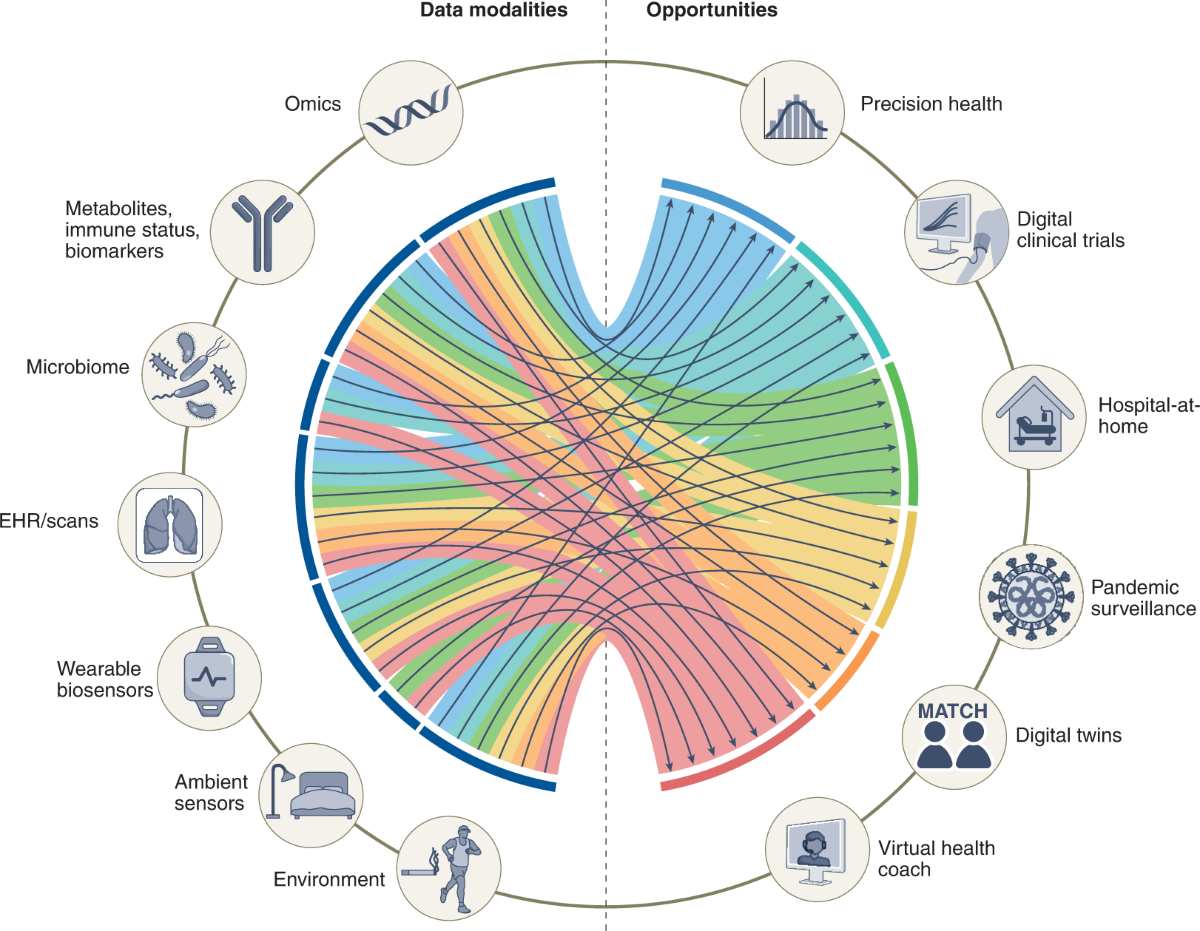
At the intersection of AI and healthcare, our biomedical research projects focus on developing intelligent, multimodal, and explainable systems to tackle real-world clinical challenges. From predicting the progression of Alzheimer’s disease to forecasting ICU patient outcomes, these works prioritize transparency, robustness, and practical deployment. Leveraging deep learning, time-series analysis, and XAI, we aim to support clinicians with trustworthy tools that improve diagnosis, prognosis, and critical care decision-making across diverse patient populations.
Traditional authentication methods—such as passwords, PINs, and even biometric systems (fingerprint, facial recognition)—typically secure mobile devices only at the point of entry. However, they fail to offer protection throughout a session, leaving devices vulnerable to unauthorized access when unattended. To bridge this security gap, the research group InfoLab at Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU) has led a series of studies on continuous, sensor-based, and adversarially-aware user authentication mechanisms.
Traditional authentication methods—such as passwords, PINs, and even biometric systems (fingerprint, facial recognition)—typically secure mobile devices only at the point of entry. However, they fail to offer protection throughout a session, leaving devices vulnerable to unauthorized access when unattended. To bridge this security gap, the research group InfoLab at Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU) has led a series of studies on continuous, sensor-based, and adversarially-aware user authentication mechanisms.

Traditional authentication methods—such as passwords, PINs, and even biometric systems (fingerprint, facial recognition)—typically secure mobile devices only at the point of entry. However, they fail to offer protection throughout a session, leaving devices vulnerable to unauthorized access when unattended. To bridge this security gap, the research group InfoLab at Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU) has led a series of studies on continuous, sensor-based, and adversarially-aware user authentication mechanisms.